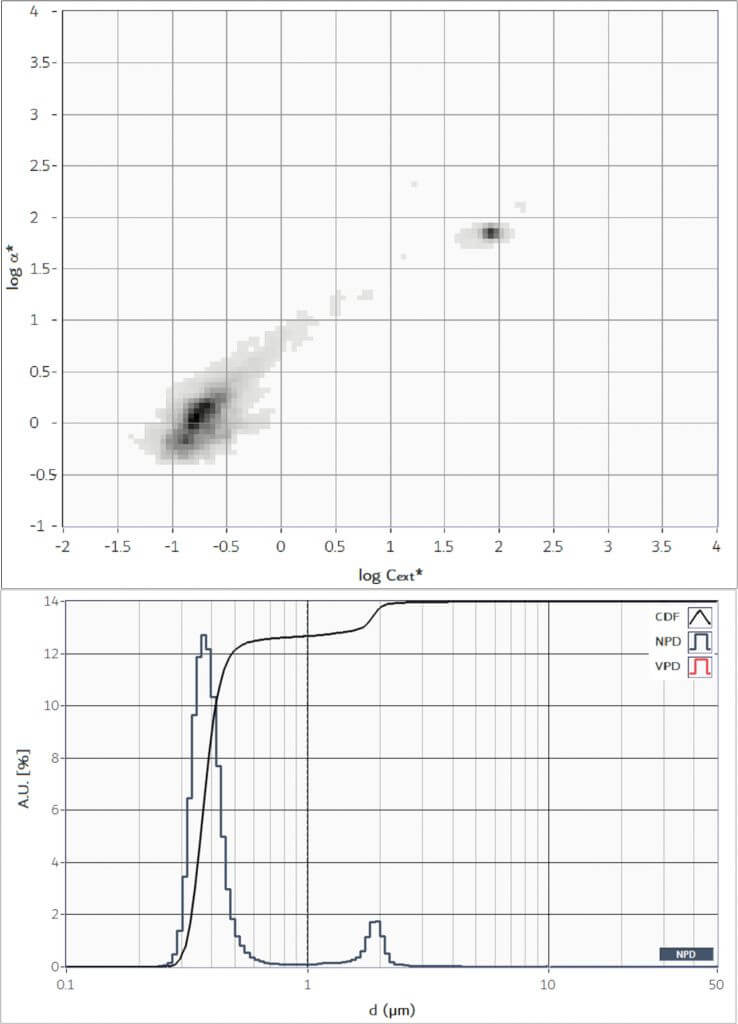
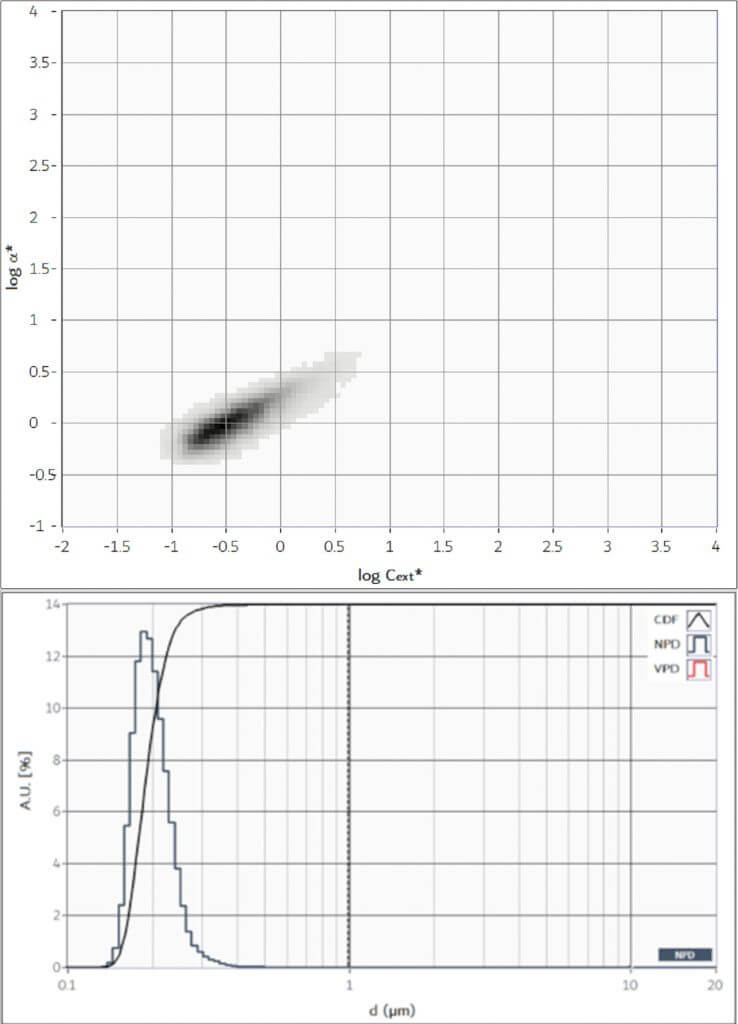
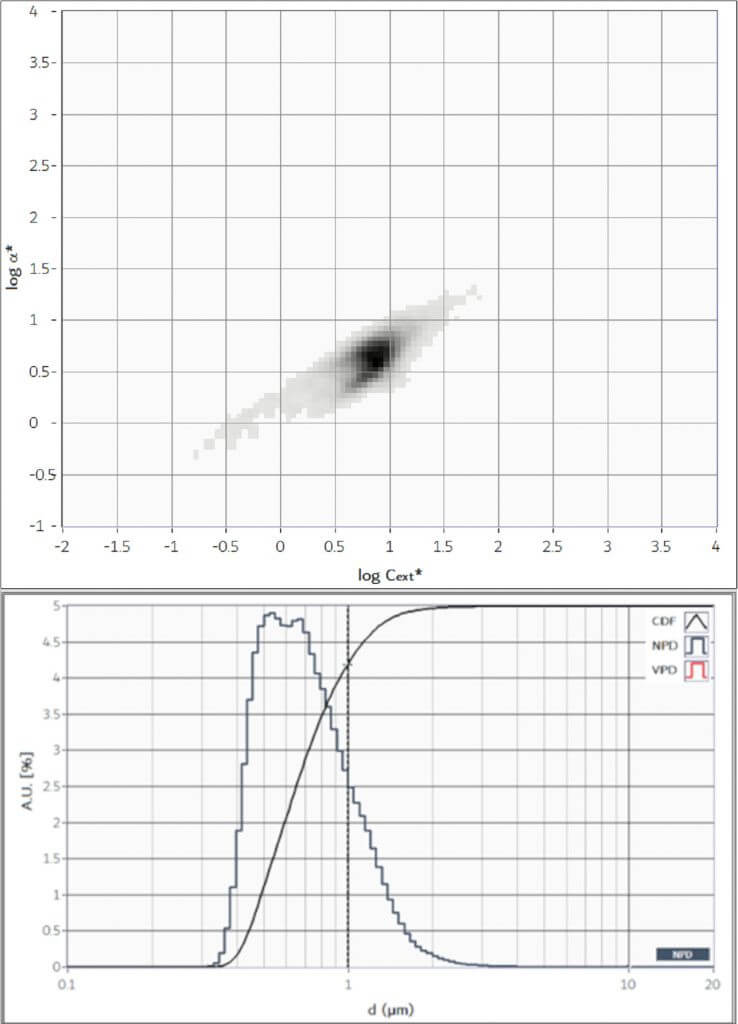
Particle characterisation of abrasives
Slurries are aqueous dispersions of compact or mesoporous particles that are essential for hi-tech technologies. Silica-based slurries are used in various industrial processes, such as the production of CDs, hard disks and the polishing of optical surfaces, among others. The properties of abrasives, such as their structure and size distribution, are crucial for their effectiveness of their operation. CLASSIZER™ ONE is an ideal tool for characterising size distribution, the density of the mesoporous structure (how compactly and evenly the pores are distributed within the abrasive) and the presence of unwanted particles (dirt, dust, etc.) or submicron aggregates.