Analyzing cell viability
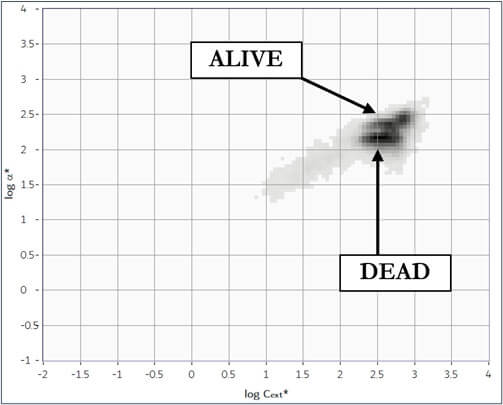
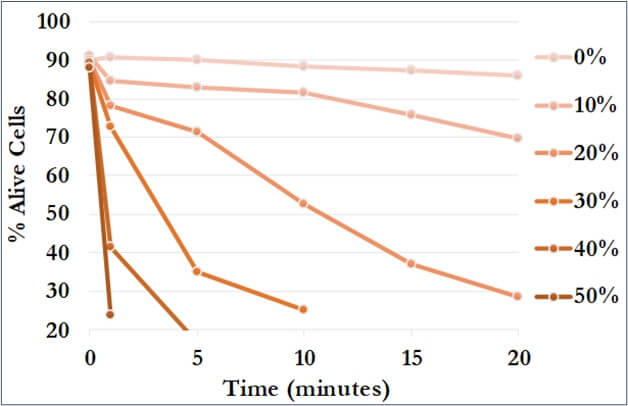
Cell viability refers to the percentage of living cells within a total population. Determining yeast cell viability is often used to investigate the effects of various stressors, both in toxicity studies and in industrial microbiology studies. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae (better known as baker's yeast or brewer's yeast) is a commonly used model organism for research into the effects of chemical, physical or environmental factors on cells. Analyzing cell viability is also crucial for industrial processes involving microorganisms used in the production of food, beverages and biofuels. The Classizer™ ONE provides accurate estimation of cell viability even in the presence of secondary populations and impurities.